New Playground for Money Laundering: Exploring the Modern Threats and Solutions
In the evolving world of finance, criminal activities such as money laundering continue to pose significant threats to both national and global economies. Over the years, authorities have made significant progress in cracking down on traditional forms of money laundering, but as technology advances, so do the methods used by criminals. In this article, we will explore the new playgrounds where money laundering is thriving, how these modern techniques work, the dangers they pose, and the regulatory efforts to combat them.
1. The Evolution of Money Laundering
Money laundering, at its core, is the process of disguising the origins of illegally obtained money, typically by means of transfers involving foreign banks or legitimate businesses. Criminals use a variety of methods to “clean” money—turning illicit funds into seemingly legitimate assets.
Historically, money laundering was associated with the physical movement of cash through underground networks, such as casinos, real estate transactions, and smuggling operations. However, with the advent of the digital age, the scope and complexity of money laundering activities have expanded. Today, technology provides a broader range of opportunities to obscure illicit financial activities.
2. The Rise of Digital Assets: Cryptocurrencies
One of the most significant developments in recent years is the use of cryptocurrencies for money laundering. Bitcoin, Ethereum, and other cryptocurrencies offer anonymity, decentralization, and the ability to quickly move large sums of money across borders without government oversight. These features, once seen as advantages of blockchain technology, have also made digital currencies an ideal tool for criminals seeking to obscure the origins of illicit funds.

How Crypto Money Laundering Works
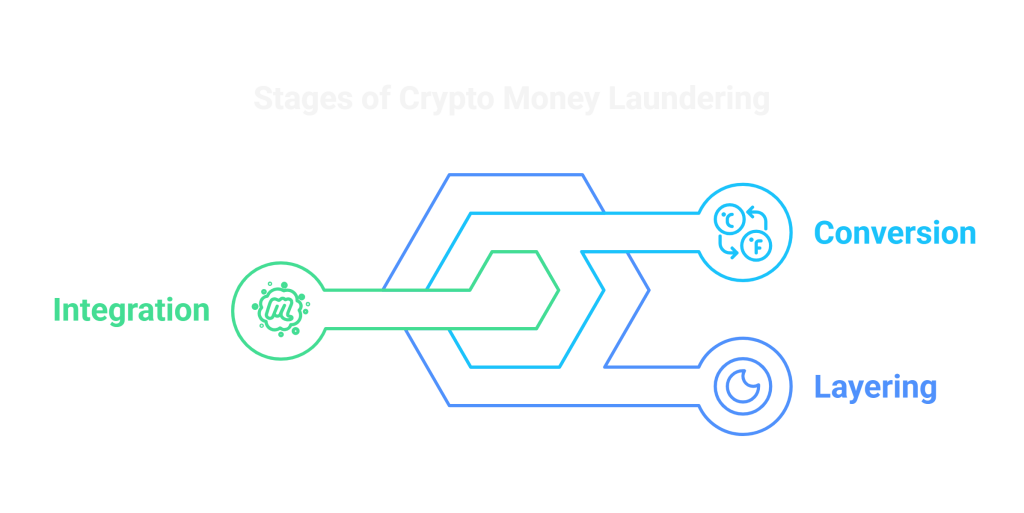
Cryptocurrencies, by their very nature, are pseudonymous. Although transactions are recorded on the blockchain, the identities behind the wallet addresses are often difficult to trace. This creates an opportunity for criminals to convert illicit money into digital currency and transfer it across borders without detection. The process typically involves three stages:
- Layering: Criminals may first exchange dirty money into cryptocurrency through a process called “mixing” or “tumbling,” which obscures the origin of the funds by mixing them with others in a large pool.
- Conversion: After the funds have been mixed, they are exchanged for other cryptocurrencies or converted into fiat currency through exchanges that may have lax Know Your Customer (KYC) protocols or no KYC at all.
- Integration: Finally, the laundered funds are reintegrated into the financial system by purchasing legitimate assets such as real estate, luxury goods, or other investments.
3. Virtual Assets and Gaming: The New Frontier
Another emerging platform for money laundering involves virtual goods and gaming. The rise of online gaming platforms and virtual worlds, such as those found in massively multiplayer online role-playing games (MMORPGs), has created a unique avenue for illicit financial activities.
In these virtual environments, players can exchange virtual currencies for real-world money or goods, a process that can be exploited for money laundering. Criminals use the game’s economy to transfer illicit funds, buy in-game items or assets, and then sell them on the open market for real money. Similarly, the use of digital marketplaces, where users can trade virtual goods, has led to the growth of laundering activities. This method allows criminals to obfuscate the origin of funds through seemingly legitimate sales.
Key Techniques in Virtual Asset Laundering
- Item Reselling: Players may buy virtual items or in-game currency with illicit funds and then resell them for real money, thus obscuring the funds’ original source.
- Money Transfers via Gaming Platforms: By using gaming platforms that support microtransactions, players can send virtual goods as gifts or pay for in-game purchases with illicit money. The recipients may then liquidate those assets.
- Trade-Based Laundering: Fraudulent trade or transactions between multiple accounts owned by the same individual are common. These transactions can artificially inflate the value of virtual goods or currency.
- Cryptocurrency-Integrated Games: Some gaming platforms allow players to earn, trade, or spend cryptocurrency in exchange for in-game achievements. This integration facilitates the movement of illicit funds between various platforms.
4. Online Marketplaces and Peer-to-Peer Platforms
The rapid rise of peer-to-peer (P2P) platforms and online marketplaces like eBay, Craigslist, and even social media groups has provided new avenues for money laundering. These platforms enable individuals to buy and sell goods and services without much oversight. Criminals can exploit these platforms by using them to purchase and sell items with illicit funds.
In many cases, the sellers on these platforms may not know they are part of a laundering operation. Criminals may also use multiple fake identities to artificially inflate the value of items and conduct transactions. The anonymity offered by these platforms, combined with the speed and ease of transactions, makes them a popular tool for money launderers.
Common Tactics on Peer-to-Peer Platforms
- Overpriced or Underpriced Goods: Launderers may list high-value items at low prices or vice versa, making the transactions appear legitimate while effectively transferring illicit funds.
- Payment Redirection: Some launderers may sell items or services to a group of people with the intent of directing payment to a different account that they control, making the illicit funds difficult to trace.
- E-Commerce Sites: Criminals can exploit e-commerce sites by selling high-demand products at inflated prices to “clean” money, often through fake reviews or the manipulation of ratings and feedback.
5. The Use of Offshore Financial Institutions
Offshore financial institutions have long been a target for money laundering due to their regulatory leniency, lack of transparency, and strict privacy laws. Criminals often deposit illicit funds in these banks to obscure the source of the money before transferring it to other accounts or jurisdictions. These institutions may not have strong KYC or Anti-Money Laundering (AML) procedures, allowing criminals to exploit these loopholes.
6. The Role of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Combating Money Laundering
While money laundering tactics have evolved with technology, the same technological advancements are also being used to combat these crimes. Financial institutions, regulators, and law enforcement agencies have begun to adopt AI and machine learning tools to identify suspicious transactions, analyze patterns of behavior, and detect anomalies in real-time.
AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data and highlight irregular activities that might otherwise go unnoticed by human investigators. Machine learning systems can learn from historical money laundering cases and improve their predictive models to identify potential risks. This proactive approach is helping authorities to stay ahead of increasingly sophisticated laundering operations.
7. Regulatory and Legal Measures: A Global Response
To counter the increasing sophistication of money laundering, governments and international organizations have stepped up their regulatory efforts. Financial Action Task Force (FATF), for instance, is an international body that sets standards for anti-money laundering (AML) practices and works with countries to ensure compliance. Countries are now required to implement stricter KYC protocols, report suspicious transactions, and cooperate with international authorities.
Key Measures and Initiatives
- Stronger KYC and AML Regulations: Countries and financial institutions are adopting more stringent customer identification and verification processes. This includes enforcing AML laws, requiring businesses to monitor and report suspicious transactions, and enhancing due diligence on high-risk clients.
- Blockchain Tracking: Given the anonymity of cryptocurrencies, various blockchain tracking tools have been developed to monitor and trace cryptocurrency transactions. These tools are helping authorities follow the flow of illicit funds across digital networks.
- International Cooperation: Since money laundering is often cross-border, international cooperation has become essential. Authorities from various nations work together through bilateral agreements, international treaties, and joint operations to identify, investigate, and prosecute money laundering activities.
Conclusion
Money laundering has evolved from traditional methods involving physical cash into sophisticated digital and virtual avenues. The rise of cryptocurrencies, online marketplaces, gaming platforms, and offshore institutions has created a “new playground” for criminals to launder illicit funds. However, financial institutions, regulators, and law enforcement agencies are increasingly leveraging technology, including AI and blockchain tracking, to fight back.
As these trends continue to unfold, it is crucial for regulators to adapt to the changing landscape. Strengthening international cooperation, enhancing financial transparency, and utilizing cutting-edge technologies will be essential in combatting this global issue. The fight against money laundering is an ongoing battle, and as the techniques used by criminals grow more advanced, so too must the efforts to identify and prevent these illegal activities.